-
Actovegin
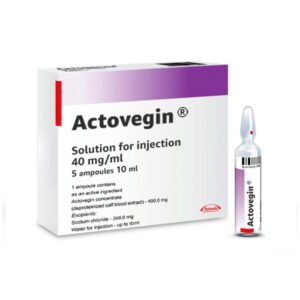
Actovegin Injections
Rated 0 out of 5$59.00 – $90.00ClearActovegin Injections 200mg N5Actovegin Injections 400mg N5Actovegin Injections 80mg N25
Types of Actovegin
The active substance of Actovegin is deproteinized hemoderivative of calf blood. Available as a solution for injections, 200mg per ampoule, 80mg per ampoule or 400mg per ampoule. Different forms are tablets, ointment, cream or gel.
Actovegin has three main modes of action – metabolic, neuroprotective and microcirculatory ameliorative effect The IFO (inositol phospho-oligosaccharides) in Actovegin oxygen utilisation and fixation, as well as energy metabolism and glucose fixation improvement. This can lead to potential benefits in tissues and organs such as the head brain injury, trauma or stroke and reduce the formation of lactate. Actovegin is thought to
the neuroprotective mechanism of action is mediated by multiple pathways: actovegine reduces amyloid beta apoptosis induced by peptides (Aß25-35) Amyloid-beta peptides are considered to be inducers of multiple molecular and cellular pathways, including oxidative stress and inflammation, which can cause nerve cell death, leading to memory loss and cognitive impairment. For nuclear medicine Factor kappa B (NF-KB) has widespread effects in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It regulates inflammation, which is the cause of many degenerative and vascular diseases and is involved in pain, learning, memory and neuroprotective processes Actovegin has been shown to activates a reporter gene for NF-KB expression in a dose-dependent manner and with this transient activation may explain, at least to some extent, the neuroprotective properties of Actovegin. Another important route is related to the nucleolar enzyme poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). PARP plays an important role in in the detection and repair of single-stranded DNA damage, but over-activation of this enzyme can initiate cellular processes that interrupt oxidative metabolism. These processes can clearly cause cell death due to energy depletion. Actovegin tablets and injections has been found to reduces PARP activity, resulting in central and peripheral nervous system functional and morphological improvement. The positive effects of Actovegin on microcirculation are associated with its ability to increase capillary blood flow velocity, reduce pericapillary area and myogenic tone of precapillary arterioles and capillary sphincters, as well as shunting of blood flow from arterioles to venules, directing blood flow mainly into the capillary bed, and to enhance microvascular endothelial oxide synthase function.Various characteristics in animal and clinical studies showed an onset of action 30 minutes after Actovegin administration. The maximum effect is reached 3 hours (2-6 hours) after parenteral or oral administration.
Actovegin is used for cerebral circulatory disorders, including cognitive impairment following stroke
disorders and dementia
Actovegin has proven benefit in dementia and dementia-related disorders symptomatic treatment in more than 450 patients in several small randomised clinical trials
studies. Efficacy compared to placebo demonstrated with cognitive function, daily target criteria related to activity and overall clinical response, while cognitive there was no statistically significant improvement in speed of functioning. 12-month, randomised, in a double-blind, placebo-controlled safety and efficacy study, the effects of Actovegin in patients who developed cognitive impairment after stroke, compared with placebo. 503
Subjects (250 of whom received Actovegin) were randomised within 5-7 days after onset of ischaemic stroke. The six-month treatment period included up to 20 infusions (2000 mg
daily), followed by tablets (2 x 200 mg three times daily) and finally at 6 months long-term observation therapy according to standard clinical practice. Subjects who received Actovegin, had statistically significant differences in the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease at 6 and 12 months and Cognitive function assessment scale (ADAS-cog+) and Montreal Cognitive Function
changes in the MoCA score compared to subjects who placebo. At months 3, 6 and 12, a higher proportion of subjects in the Actovegin group were compliant
the definition of a patient with a response according to ADAS-cpg+. . Although the overall incidence of recurrent ischaemic stroke was within the expected range for this patient population, a higher incidence was observed in the Actovegin group than in the placebo group.
Actovegin products effects on disorders of peripheral blood flow and its sequelae
In a series of small comparative randomised trials in 190 patients with peripheral arterial peripheral circulatory disorders and their sequelae were treated with
Actovegin. These studies found a short-term benefit for Actovegin infusion compared with placebo benefits. In terms of distance walked, the Actovegin treatment group showed an improvement of
35 – 42% compared to placebo. In an open, randomised trial of 60 patients with extensive venous shin ulcers received standard treatment with or without Actovegin. Actovegin was administered daily intravenous infusions of 250 ml of a 10% solution for four weeks. The healing times in the groups were 31 (Actovegin) and 42 days, respectively. Compared to baseline levels, pain scores improved in both groups – from 4.47 to 1.77 in the Actovegin group, and from 4.47 to 1.77 in the in the study group from 4.13 to 2.07.
Actovegin effects on diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN)
Study in 70 patients with diabetic polyneuropathy showed statistically significant benefit distance, nerve conduction velocity (NCV) and pain sensitivity statistically significant changes in Actovegin-treated patients compared to placebo. Placebo-adjusted treatment effect was approximately 6.5 m in terms of distance walked, 0.9 m/s in terms of NCV and 6.8 in terms of pain sensation (on a 100-point scale). Six months,
a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled safety and efficacy study 567 patients with type 2 diabetes and symptomatic diabetic distal polyneuropathy received 20 Actovegin i.v. infusions (2000 mg daily) (n=281) or placebo (n=286) once daily no for more than 36 days, followed by 3 tablets of Actovegin (1800 mg daily) or placebo three times per day for another 140 days. For the primary endpoint – Total Symptom Score (TSS; Total Symptom Score), including positive neuropathic symptoms (pain, burning sensation, paresthesia and numbness) in the feet or legs, Actovegin was superior to placebo. The distribution of adverse events between treatment and control groups was significantly were no different.
Pharmacokinetic studies of absorption, dispersion and elimination by chemo-analytical methods cannot be performed on Actovegin because the active ingredients are physiological substances that normally occur in the body.
Preclinical safety data
Data from non-clinical studies on repeated dose toxicity, reproductive toxicity, mutagenicity, immunotoxicity and contact allergenicity do not indicate a particular risk to humans. Animal studies have shown that even at doses up to 30-40 times the respective human doses, this deproteinised calf blood derivative does not cause local and/or systemic toxicity after single or repeated oral, dermal, subcutaneous or intravenous administration.
Actovegin solution is administered intravenously (including infusion), intra-arterially, and also intramuscularly.
Injection rate: slow (2 ml/min).
Due to the possibility of serious anaphylactic reactions, it is recommended to perform an allergic test before administration (2 ml intramuscularly).
Our Happy Clients!